FLOWCHART
The
flowchart is a means of visually presenting the flow of data through an
information processing systems, the operations performed within the system and
the sequence in which they are performed.
The program flowchart can be likened to the blueprint of a
building. The flowchart is drawn according to defined rules and using standard
flowchart symbols prescribed by the American National Standard Institute, Inc.
Def:
A flowchart is a diagrammatic
representation that illustrates the sequence of operations to be performed to
get the solution of a problem.
·
Flowcharts
are generally drawn in the early stages of formulating computer solutions.
·
Flowcharts
facilitate communication between programmers and business people.
·
The
flowcharts play a vital role in the programming of a problem and are quite
helpful in understanding the logic of complicated and lengthy problems.
Guidelines for Drawing a Flowchart
Flowcharts are usually drawn using
some standard symbols; however, some special symbols can also be developed when
required. Some standard symbols, which are frequently required for flowcharting
many computer programs are shown in Fig.
Fig
15: Flowchart
Symbols
Advantages
of using Flowcharts
The
benefits of flowcharts are as follows:
1.
Communication: Flowcharts are better way of
communicating the logic of a system to all concerned.
2.
Effective analysis: With the help of flowchart, problem
can be analyzed in more effective way.
3.
Proper documentation: Program flowcharts serve as a good
program documentation, which is needed for various purposes.
4.
Efficient Coding: The flowcharts act as a guide or
blueprint during the systems analysis and program development phase.
5.
Proper Debugging: The flowchart helps in debugging
process.
6.
Efficient Program Maintenance: The maintenance of operating
program becomes easy with the help of flowchart. It helps the programmer to put
efforts more efficiently on that part.
Limitations
of using Flowcharts
1.
Complex logic: Sometimes, the program logic is
quite complicated. In that case, flowchart becomes complex and clumsy.
2.
Alterations and Modifications: If alterations are required the
flowchart may require re-drawing completely.
3.
Reproduction: As the flowchart symbols cannot be
typed, reproduction of flowchart becomes a problem.
The
essentials of what is done can easily be lost in the technical details of how
it is done.
Few
examples of flowcharts
1. To
find the sum and average of 3 numbers.
2. To
find simple interest.
3. To
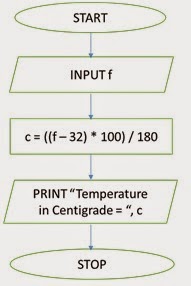
convert Fahrenheit temperature to centigrade
4. To
swap two numbers using a third variable
5. To
swap two numbers without using a third variable
6. To
find whether the number is odd or even.
7. To
check whether the roots of quadratic equation are real or imaginary.
8. To
find the largest among given two numbers.
9. To
find the largest among given three numbers.
10. To
find the sum of the digits of n-digit number.
11. To
reverse the digits of given n-digit number.
12. To print
numbers divisible by 7 from 1 to N numbers.
13. To
calculate the factorial of a number.
14. To
find whether a given number is prime or not.
15. To
print first N Fibonacci numbers.















No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.